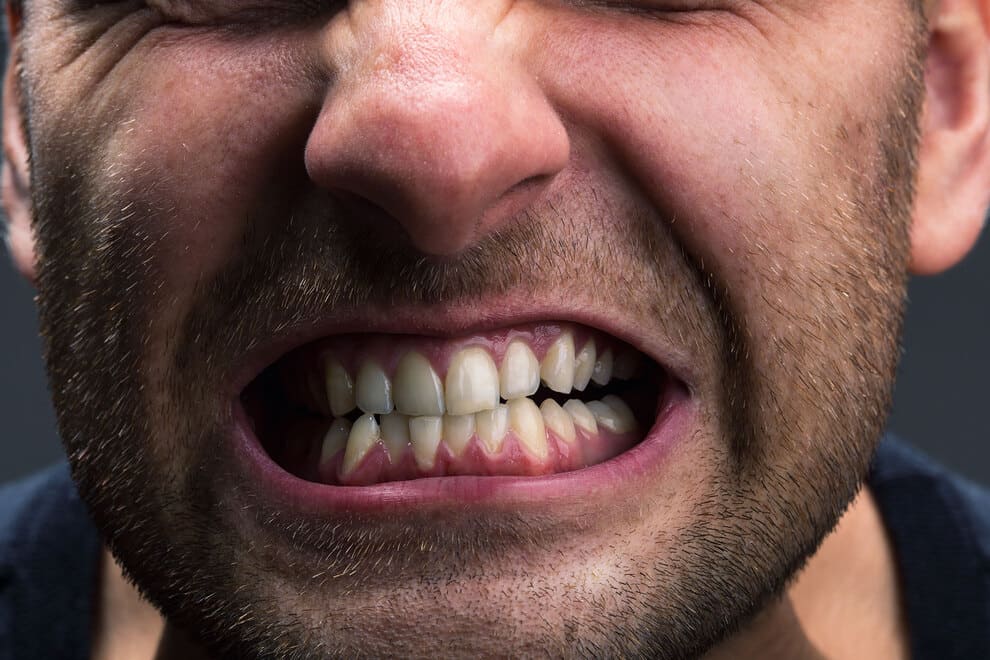
Stress teeth grinding is more than just an annoying habit; it’s a sign that your body is struggling to cope with tension. Many individuals are not even aware they grind or clench their teeth until they experience jaw pain, morning headaches, or tooth wear
When left unchecked, this stress-driven behavior may have long-term harmful consequences, ranging from chipping teeth to developing jaw joint disorders. Fortunately, with the right strategies, you can break the cycle, protect your smile, and find relief.
In this blog, we’ll explore what bruxism is, the most common causes, key symptoms to watch for, and effective treatments and tips to help you stop grinding your teeth and protect your oral health.
What Is bruxism? understanding the condition
The medical name for clenching, grinding, or gnashing of teeth is known as bruxism, usually done without awareness. It may occur during the day when you are awake or at night while you sleep.
It is quite normal to grind your teeth occasionally, especially when you are experiencing stress or anxiety. But if you are grinding frequently or severely, dental complications can arise from the extra strain and pressure put on your teeth and jaw.
Although anyone can develop bruxism, it is most commonly seen in children, teens, and young adults. Since sleep bruxism happens when you’re unconscious, many people aren’t aware of the habit until a dentist notices until symptoms appear.
Types of bruxism
-
Clenching Teeth While Awake
It refers to the act of grinding or clenching your teeth while you’re awake during the day. It often happens when you’re stressed, anxious, angry, or intensively focused on something.. Many people notice themselves clenching their jaw while working, focusing, or dealing with stressful situations.
Because you’re conscious, this type is easier to manage. In mild cases, treatment may not be necessary if you can control the clenching on your own.
-
Sleep bruxism
Sleep bruxism happens when you unknowingly grind or clench your teeth while you’re sleeping. It’s tricky to manage or stop because it’s not something you’re aware of doing. Since it goes on at night, many folks don’t realize they have it until they notice signs of tooth wear.
Sleep bruxism is often considered more damaging than awake bruxism, as it puts intense, constant pressure on your teeth and jaw joints without you even realizing it. That’s a big reason why treatment is frequently suggested. This is why treatment is often recommended.
Common causes of teeth grinding while sleeping
Bruxism does not have a single cause. Rather, teeth grinding during sleep is associated with a variety of physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors. Understanding their effects can help you cope with the bruxism and protect your teeth.
Main Risk Factors:
- Stress and anxiety: These are among the biggest triggers. People with anxiety or depression generally are more prone to bruxism.
- Lifestyle habits: Such as smoking, drinking alcohol and heavy caffeine use increase the risk.
- Sleep disorders: There has been a strong link established between bruxism and sleep apnea; however, research is still ongoing to understand the relationship more clearly.
- Jaw alignment issues: Misaligned bite or teeth can contribute.
- Age: More common in children, teens, and young adults.
Key symptoms of teeth grinding
- Grinding or clenching noises at night (sometimes loud enough to wake a partner)
- Flattened, chipped, or loose teeth
- Worn tooth enamel that exposes inner layers
- Tooth pain or sensitivity
- Tight or tired jaw muscles, or a jaw that feels “locked”
- Enlarged jaw muscles (from constant clenching)
- Dull headaches, often starting at the temples
- Sleep problems, including poor sleep quality
Stress and teeth grinding: relation between stress and bruxism
One of the major triggers for bruxism is stress; individuals with chronic stress or anxiety are more likely to clench their jaws or grind their teeth at night. When you are under stress, your body releases stress hormones; in turn, your muscles become tense, which can lead you to grind or clench your teeth unconsciously. Stress also affects your sleep, keeping you in lighter stages where grinding happens more often. All of this means that stress management is crucial to preventing damage to the teeth and jaw.
Effects and complications of untreated bruxism
Ignoring stress teeth grinding, you might end up dealing with some serious, long-term issues. Over time, that non-stop clenching and grinding can:
- Damage teeth: Causing the enamel to wear down, leading to chips, cracks, or even loose teeth.
- Trigger TMJ disorders: Leading to long-term jaw discomfort, times of clicking, and inability to open or close your mouth.
- Cause ongoing facial pain or headaches: Which may affect your daily comfort and focus.
- Disrupt sleep: Causing you to still feel tired and less rested, even after a full night of sleep.
Best treatment options for stress-related bruxism
Occasional grinding isn’t a huge problem and might not require any treatment. However, if you’re dealing with pain, notice damage to your teeth, or frequent grinding, these options can help protect your teeth and jaw:
- Custom Mouth Guards: Your dentist can make a special night guard for you. It fits over your teeth while you sleep, acting like a cushion to protect them and helping keep your jaw in a more relaxed position. This can ease the strain on your jaw muscles and the joint that connects your jaw (TMJ).
- Stress-Reduction Techniques: Managing stress is one of the most effective ways to stop bruxism. Techniques like meditation, yoga, exercise, or breathing exercises can help relax your jaw and calm your nervous system.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Reduce or eliminate caffeine (especially before sleeping), and quit smoking if possible. These habits are strongly associated with increased grinding.
- Medication (Short-Term): In some cases, doctors may prescribe a muscle relaxant before bedtime to ease jaw tension. This is usually a temporary solution.
Tips to reduce stress and stop teeth grinding
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Relax before bed with deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or progressive muscle relaxation to ease any jaw tension.
- Improve Sleep Hygiene: Keep a consistent bedtime, limit screen time before sleep, and create a calming nighttime routine to get deeper, more restorative rest.
- Do Jaw Stretches: Simple exercises suggested by a dentist or physical therapist can help loosen up tightness in your jaw.
- Manage Stress Daily: Light exercise, or short breaks during work can keep stress hormones in check.
- Avoid Triggers at Night: Avoid caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine in the evening. These all can increase grinding at night.
- Schedule Regular Dental Checkups: Your dentist can identify early signs of teeth grinding and help prevent small issues from developing into serious dental issues by Regular Dental Checkups.
When to seek professional help
If your stress teeth grinding is causing pain, cracked teeth or interfering with your sleep, you should see a specialist. Early intervention can help you avoid long-term consequences on your teeth and jaw.
At El-Shenawy Dental Clinics, our team specializes in diagnosing and treating bruxism. We offer:
- A thorough examination to identify tooth wear, jaw tension, and TMJ issues.
- Custom night guards that are made to protect your teeth and reduce the strain on your muscles.
- Personalized treatment plans that address both the dental and stress-related aspects of bruxism.
Book your consultation today and discover the best solution for your teeth grinding.
Frequently asked questions
-
Is teeth grinding normal?
Occasional teeth grinding might just be normal, especially when you’re under a lot of stress. However, if you experience frequent grinding , particularly while you sleep, it can actually harm your teeth and jaw and it should be addressed by a dentist.
-
What’s the difference between clenching and grinding?
Clenching means holding your teeth tightly together, while grinding involves sliding them back and forth. Both put pressure on teeth and jaw muscles.