Sugar is a part of so many foods and drinks we enjoy, but it’s also one of the biggest contributors to dental problems.From a very young age, we’re warned about the link between sugar and teeth health. The more often you consume sugar, and the longer it lingers on your teeth, the greater the harm it can cause. Understanding exactly how sugar impacts your oral health is the first step toward making smarter choices and protecting your smile from its hidden dangers.
Sugar and teeth: how sugar fuels tooth decay
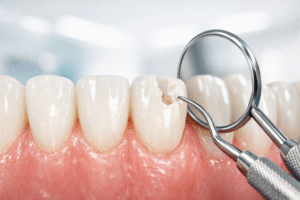
Whenever you eat a sugar-rich treat, the bacteria in your mouth start to act on that sugar and produce acids that attack your teeth’s enamel. That puts your teeth in a constant state of acid exposure. This ongoing acid exposure leads to demineralization, which is the very first step towards tooth decay.If we don’t stop this process, the enamel becomes weaker, begins to degrade, and eventually, cavities appear.
The World Health Organization (WHO) points out a clear connection between how much sugar we eat and our chances of getting cavities. They suggest that we should keep added sugars to less than 10% of our daily calories, and ideally, aim for no more than 5%. This advice covers both the obvious stuff, like candy and soda, as well as hidden sources such as fruit juices, honey, and sweetened sauces. That’s because mouth bacteria make no distinction between natural and refined sugars.
Choosing sugar-free options can help shield your teeth because they do not produce acids that erode enamel. When used along with good oral hygiene methods and regular check-ups, these habits can greatly limit the damage sugar can do.
Beyond cavities: does sugar only cause decay?
Cavities are the most well-known consequence of sugar, but its harm doesn’t stop there. Sugar feeds harmful bacteria, which may negatively impact several areas of your oral health:
- Gum inflammation (gingivitis): Bacteria feed on sugar and irritate your gums, causing redness and swelling.
- Periodontal disease: If gum issues aren’t treated, they can get worse and eventually harm the bones and tissues that support your teeth.
- Tooth sensitivity: Frequent acid attacks erode enamel, making teeth more sensitive to hot, cold, or sweet foods.
- Wear and discoloration of the enamel: When enamel breaks down, teeth may appear yellow and dull.
- Impact on developing teeth: A child’s permanent teeth’s strength and health may be impacted by a high sugar intake.
Risk factors that make sugar damage worse
- Poor oral hygiene: If you don’t brush and floss regularly, plaque builds up, giving sugar more time to fuel acid attacks
- Dry mouth: When you don’t produce enough saliva, you have fewer natural defenses to wash away sugars and balance out the acids in your mouth.
- Smoking and tobacco use: Reduces saliva production, weakens gum health, and slows healing, making sugar-related damage more severe.
- Acidic diets: Enamel erosion is accelerated when sugar is combined with acidic foods or beverages (such as soda, citrous juices, or energy drinks).
- Pre-existing dental conditions: Your teeth are more vulnerable to sugar damage if you have weak enamel, gum disease, or previous dental work.
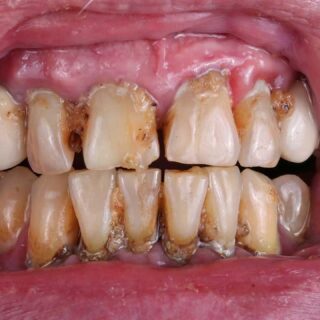
Long-term complications of untreated sugar damage
If teeth hurt when eating sugar and the issue is left untreated, it can lead to serious complications including:
- Severe tooth decay: Cavities can grow deeper, eventually reaching the tooth’s pulp and requiring root canal treatment or extraction.
- Gum disease: The same kind of bacteria that cause cavities can also irritate your gums. This irritation can lead to gingivitis (inflamed gums). With no treatment, it can worsen and turn into periodontitis, which is a more serious gum disease.
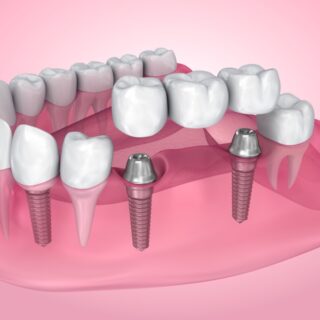
- Tooth loss: When decay gets worse or gum disease becomes severe, it can seriously weaken the structures that hold your teeth in place. This might make your teeth feel loose, or in the worst cases, they could actually fall out.
- Infections and abscesses: Bacterial infections may spread beyond the tooth, leading to painful abscesses and even systemic health risks.
- Bite and alignment issues: Over time, shifting, bite issues, and jaw discomfort can result from missing or damaged teeth..
- Impact on overall health: Poor oral health has been linked to heart disease, diabetes complications, and other systemic conditions.
Simple habits to minimize sugar-related tooth problems
- Control sugary treats and drinks: Make them occasional treats instead of daily habits.
- Choose sugar-free alternatives: Opt for snacks or gum with xylitol or stevia, which don’t feed harmful bacteria.
- Rinse or brush after sugar: If you can’t immediately brush your teeth, rinse your mouth with water to wash away sugar and acids.
- Maintain regular brushing and flossing: To get rid of plaque, use fluoride toothpaste twice a day and floss every day.
- Remain hydrated: Water encourages saliva, which in turn naturally protects teeth.
- Be mindful of hidden sugars: Read labels to identify sugars in sauces, processed foods, and beverages.
Key symptoms that mean you need a dentist
Ignoring early signs of sugar and teeth problems can lead to more complex issues later. Regular dental checkups are equally important, as they help spot and address concerns before they escalate. Here are some symptoms to watch for:
- Persistent tooth pain or sensitivity: Persistent bad breath: It can indicate decay, gum disease or something worse.
- Teeth sensitive to sugar: This discomfort often indicates cavities, enamel erosion, or exposed dentin. If your teeth react to sugary foods or drinks, it’s a clear sign you should visit a dentist.
- Bleeding gums: Often a sign of gum disease, especially if accompanied by swelling.
- Bad breath that doesn’t go away: May indicate decay, gum disease, or other underlying issues.
- Loose or shifting teeth: Could point to advanced gum disease or bone loss.
- Mouth sores that don’t heal: Important to have checked, as they can sometimes indicate more serious health concerns.
- Changes in bite or jaw discomfort: Could signal TMJ issues or teeth grinding.
At El-Shenawy Dental Centers, we provide advanced tooth cavity treatments designed to stop decay and restore your smile’s health.
El-Shenawy dental centers: tailored solutions for every smile
At El-Shenawy Dental Centers, our experienced team combines advanced diagnostics with personalized care to tackle the effects of sugar and teeth issues before they escalate. We emphasize prevention and early detection, and we treat issues promptly and effectively. By combining state-of-the-art technology with compassionate expertise, we offer treatments tailored to your specific needs. Our absolute commitment is to safeguard your smile and preserve it for the long term.
Book your appointment today now and enjoy stronger, healthier teeth for years to come.
Frequently asked questions
-
Is natural sugar capable of causing the same damage as processed sugar
Yes. No matter where it comes from, whether candy or fruit juice, your mouth bacteria turns all sugars into acid that can hurt your teeth.
-
Can sugar-sensitive teeth be reversed?
In some cases, sensitivity can be treated by reducing its sensitivity using treatments such as fluoride application, fillings, or dental sealants, depending on the cause.